Water Resource Management
Basic approach
Recognizing that water resources are one of the important natural assets, artience group is working to reduce water consumption and wastewater, reduce the impact of wastewater on the environment and living organisms, and identify and reduce water risks that affect business continuity.
In addition to ASV2050/2030, we have established Group Materiality 2025-2030 (formulated in February 2025), and have set medium- to long-term goals, KPIs, and measures for water management. To achieve this goal, we will reduce water consumption by thoroughly implementing circulating cooling and reducing water consumption through post-use reuse and recycling, as well as by developing production processes that do not require water.
Targets and achievements
Targets
Achievements
In FY2024, water consumption in Japan was 2,632 thousand m3 (up 5.1% from the previous year), of which 94.0% was groundwater. In addition, the water consumption of overseas affiliates was 1,332 thousand m3, a decrease from the previous fiscal year.

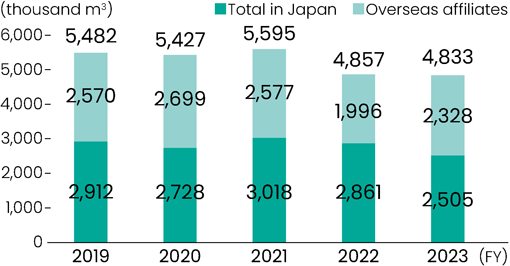
Scope of aggregation: Major domestic manufacturing plants and factories and domestic affiliates, overseas major overseas production affiliates
* The figures have been revised due to errors in the 2023 tally of overseas affiliates
- Water Recycling and Efficient Water Utilization
- Prevention of water pollution
Risk management
In order to understand the risks related to water use and to respond to water risks, the Group uses the World Resources Institute's Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas version 4.0 to assess quantitative, qualitative, regulatory, and reputational risks at the basin level for groups in Japan and overseas.
In preparation for "water stress" and "water demand" that are expected to worsen in the future, as indicated by the evaluation results, we will continue to work to effectively use water and reduce the amount of water used.
Water risk assessment and response
As a result of Akiduct's evaluation, none of the sites in Japan rated the overall water risk as "High" ~ "Extremely High", and the quantitative risk was "high" at 7 sites. On the other hand, in Asia other than Japan (Southeast Asia, India, China, Taiwan, and South Korea), more than half of our sites rated their overall water, quantitative, and qualitative risks as "high ~ significantly high." In particular, the risk of "water stress" is significantly higher in Thailand and India, the "river flood risk" is high in Vietnam and Indonesia, and the "coastal flood risk" is significantly higher in the South China region of China. Qualitative risk is also shown to be significantly higher in Southeast Asia and India.
Akiduct's 2030 forecast for the BAU (BAU) scenario shows that the risk of "water stress" will worsen at 17 sites and the risk of "water demand" at 24 sites. In particular, water stress is evaluated as a "prediction of significant deterioration" in Thailand and India.
Based on the results of the assessment, we are preparing for flooding at sites with high flood risk by implementing measures taken by TOYO INK (THAILAND) CO., LTD., which has experienced large-scale floods in the past, including relocation of electrical equipment, installation of sandbags, and clarification of procedures for cutting off electricity.
| region |
business |
Comprehensive Water Risks |
quantitative risk |
qualitative risk |
Regulatory Risks Reputational risk |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| water stress |
Water exhaustion |
season fluctuation |
Groundwater level Decline in |
Rivers Flood risk |
Coastal Flood risk |
Drought risk |
Unprocessed Connected drainage |
||||||
| Japan | 13 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Asia (Except Japan) |
21 | 12 | 14 | 9 | 4 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 12 | 15 | 4 |
| Europe | 4 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| North America/Central and South America | 5 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| total | 43 | 13 | 27 | 14 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 12 | 15 | 4 |
