What is bioplastic?

- Definition of bioplastic
- Biomass pressure sensitive adhesives
- biodegradable pressure sensitive adhesives
Definition of bioplastic
"Biodegradable plastics" that are biodegraded by microorganisms and "biomass plastics" that are manufactured from biomass are collectively called "bioplastics."
- Japan Bioplastics Association (JBPA): A private organization established in 1989
Related environmental issues
← Biomass biodegradation →
| global warming | Oil-free raw materials | Recycling society | ocean plastic trash |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reduction of petroleum-based CO2 emission by bioplastic carbon neutral | Reduce dependence on fossil resources and improve resource circulation by switching from exhaustible petroleum to renewable resources (biomass) | Improving recycling rate by switching from incineration of plastic waste to biological treatment (composting/gasification) | Reducing the impact of marine plastic debris on the marine environment |
Flow of environmental response in base material (film)
Efforts are also being made to be environmentally friendly by using bioplastic raw materials for plastic base materials (films).
| polylactic acid | cellulose | starch |
|---|---|---|
| It is a plant-derived biodegradable bioplastic that is becoming more and more popular around the world. |
A bioplastic derived from wood pulp that is biodegradable in the ocean. It is processed into films, non-woven fabrics, etc. |
It is derived from plants and is biodegradable. It is expected to be used as a bioplastic that is inexpensive and can be mass-produced. |
pressure sensitive adhesives is applied to the base material shown above and processed into labels, tapes, etc.

Examples of plant-derived raw materials

Examples of labels and tapes
Biomass pressure sensitive adhesives
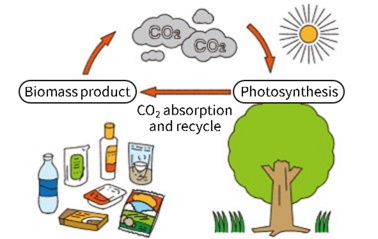
Biomass pressure sensitive adhesives are able to reduce CO2 more than existing normal products. It is causative substance of global warming, but plants as raw material absorb CO2 when they grow up. Therefore it will not increase as total if you burn final adhesive coated product for dispose. This concept is based on "Carbon neutrality".
Click here for our biomass pressure sensitive adhesives products
Biomass pressure sensitive adhesives
biodegradable pressure sensitive adhesives
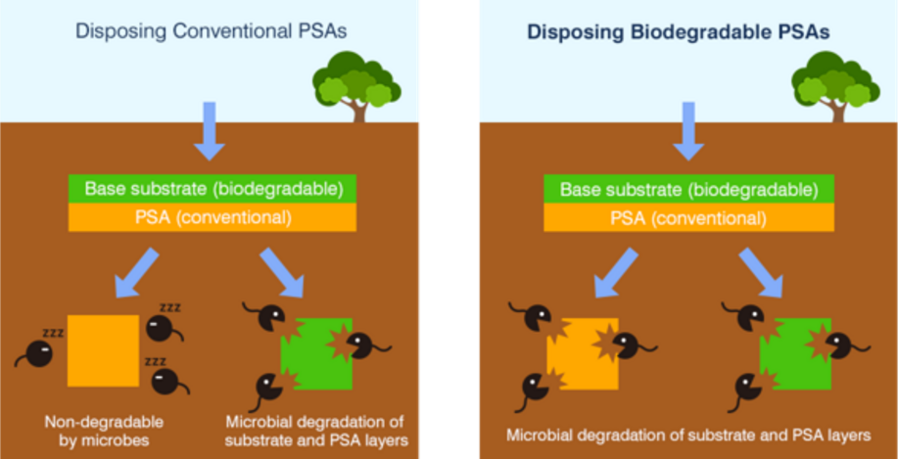
It is possible to impart biodegradability to the entire product.
Unlike conventional products, by using our biodegradable pressure sensitive adhesives as a set, it becomes possible to make the entire product biodegradable and environmentally friendly.
Click here for our biodegradable pressure sensitive adhesives products
Environmentally friendly pressure sensitive adhesives with biodegradability of over 90%
About biodegradability test
The following biodegradability test methods have been published by ISO, and JIS standards corresponding to each have been published.
- Compost decomposition: Decomposes in special equipment (high temperature and humidity)
ISO 14855-1 (JIS K6953-1)
→ TOYOCHEM: Biodegradable pressure sensitive adhesives, Toyo-Morton: Biodegradable adhesives
ISO 14855-2 (JIS K6953-2) - Soil decomposition: decomposition in soil
ISO 17556 (JIS K6955) - Aqueous decomposition: decomposes under freshwater conditions
ISO 14851 (JIS K6950)
ISO 14852 (JIS K6951) - Marine biodegradation: decomposition in seawater
ISO 18830
ISO 19679
* Both are compatible, and there is no JIS standard.
About marine biodegradation test
About marine biodegradation
TUV Austria: A private certification body that certifies marine biodegradation.
In laboratory tests, 27 products (as of March 2020) have been certified to biodegrade by more than 90% within 6 months in seawater at 30°C and meet various conditions (non-toxicity, etc.).
About the difference in biodegradation
The amount of bacteria varies depending on the environment. Biodegradation progresses relatively easily in environments where large amounts of bacteria exist, such as in compost environments, garbage (activated sludge), and soil.
➝There are very few bacteria in seawater, making it difficult for biodegradation to proceed.
Expected uses of biodegradability (examples)
Fields used in the natural environment (natural processes)
Soil decomposition, aqueous decomposition, marine biodegradation

(Multi-purpose film, seedling pots for transplanting, fishing line, fishing net, seaweed net, etc.)
・Civil engineering/construction materials
(Water-retaining materials for greening wastelands and deserts, sandbags, water-retaining sheets for construction, vegetation nets, etc.)
・Outdoor leisure supplies
(Disposable products for golf, fishing, marine sports, etc.)
・Water treatment materials
(precipitant, dispersant, detergent)
Fields useful for composting organic waste (artificial processes)
Compost decomposition etc.

(Fresh food trays, fast food containers, lunch boxes, etc.)
・Hygiene products
(Disposable diapers, sanitary products, bandages, etc.)
Daily necessities, miscellaneous goods
(garbage bags, disposable cups, etc.)
Inquiries
TOYOCHEM CO., LTD. Packaging and Industrial Materials Sales Division Sales Department 1
TEL:+81-3-3272-0940
