Sintered silver nano bonding material
This is a sintered silver nano bonding material that achieves strong bonding strength, high thermal conductivity, and printability using unique silver nanoparticle design and paste design technology.
Development product overview
As power semiconductors are attracting attention in order to realize a decarbonized society, we are working on the development of a sintered silver nanobonding material as a new bonding material to replace conventional solder materials.
Bonding materials must be lead-free from the viewpoint of toxicity to the human body and environmental impact. In addition, power semiconductors must be driven in high-temperature environments due to the increase in current and density, so they are required to have better heat resistance and heat dissipation than ever before.
To address these issues, our group is developing a sintered silver nano bonding material with excellent heat dissipation by controlling the density of the bonding coating.
Features of the developed product
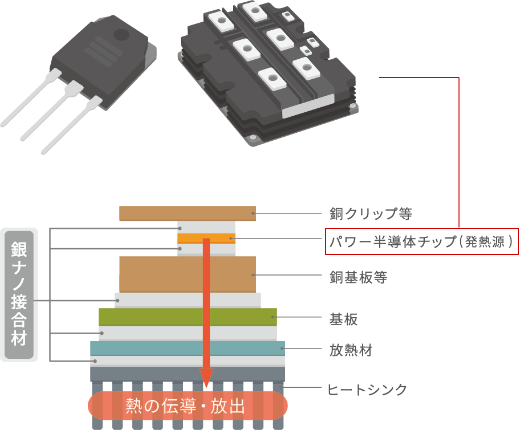
[Next generation power device]
Si (operating temperature: 150-190℃)
⇒ SiC (operating temperature: 200-300℃)
Current solder has a melting point of 220℃, so
Insufficient heat resistance. On the other hand, sintered silver
It has a melting point of approximately 960℃.
- Achieves extremely high thermal conductivity of 300W/m・k or more
- Achieves strong joints with a joint strength of 40 MPa or more through pressureless sintering
(There is no need to introduce a pressure device. It can be applied to materials that are not suitable for pressure. However, it is also compatible with pressure sintering processes.) - Achieves excellent metal mask printing and dispense printing
Characteristics of the developed product
Paste physical properties
| Development product | Solder (lead free) | |
|---|---|---|
| silver content | 87% or more | ー |
| viscosity | 20~100Pa・s | ー |
Bonding conditions
| Development product | Solder (lead free) | |
|---|---|---|
| Bonding pressure | No pressure or pressure | No pressure |
| Junction temperature | 230℃~300℃ | >320℃ |
| Sintering atmosphere | Air, N2 | Air, N2 |
| joint surface | Au, Ag, Cu | Au, Ag, Cu |
Bonding layer properties
| Development product | Solder (lead free) | Measuring method | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bonding strength | >40MPa | 32MPa | Measured with die shear meter |
| heat cycle | >1000cyc | ー | -40℃30 minutes↔150℃30 minutes |
| High temperature resistance | >400℃ | 220℃ (melting point) | ー |
| electrical resistance | 3μΩ・cm | 13μΩ・cm | 2-terminal measurement method |
| Thermal conductivity | 300W/m・k | 65W/m・k | laser flash method |
Sample composition: 5mm□chip/bonding layer/base material
Features of the developed product
Application example
It is useful for die bonding, die attach, submount, and package joining in power semiconductors, radio frequency devices (RF), light emitting diodes (LEDs), and semiconductor lasers (LDs) that require high temperature operation.
In addition, it can be used not only for bonding under chips and heat sinks, but also for areas with complex shapes that are difficult to apply pressure to.


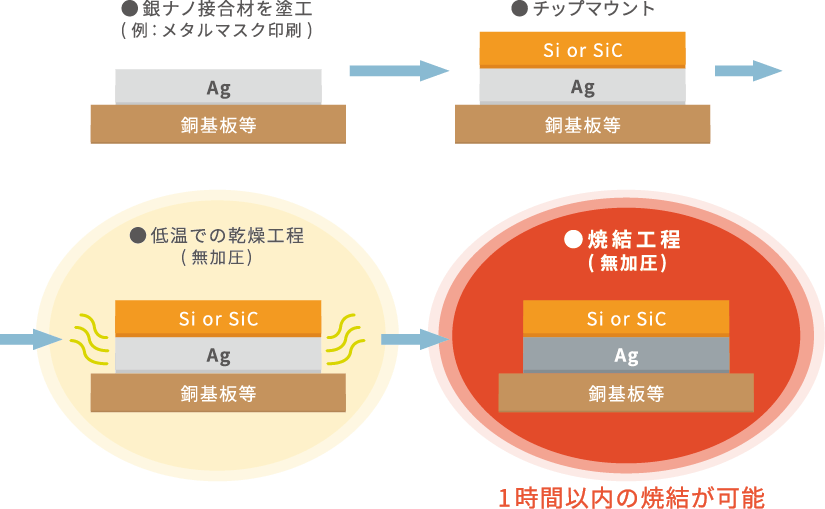
Technology overview
Unique silver nanoparticle design technology and paste design technology that achieves printability
In this development, we leveraged our technological foundations of ``proprietary silver nanoparticle design technology'' and ``paste design technology (dispersion technology and coating film densification technology)'' to achieve the excellent bonding strength of pressure-free sintered silver. It exhibits physical properties such as high reliability and high heat dissipation.
It is also compatible with printing methods such as metal masks and dispense, and its excellent viscosity properties provide printability with process benefits that minimize the amount of paste waste.
Unique silver nanoparticle design technology
Silver nanoparticles are nano-sized silver particles. The melting point of silver is 962°C, but by making it into nanoparticles, the melting point is lowered, making it possible to sinter at temperatures over 200°C. This achieves properties such as thermal conductivity and bond strength.
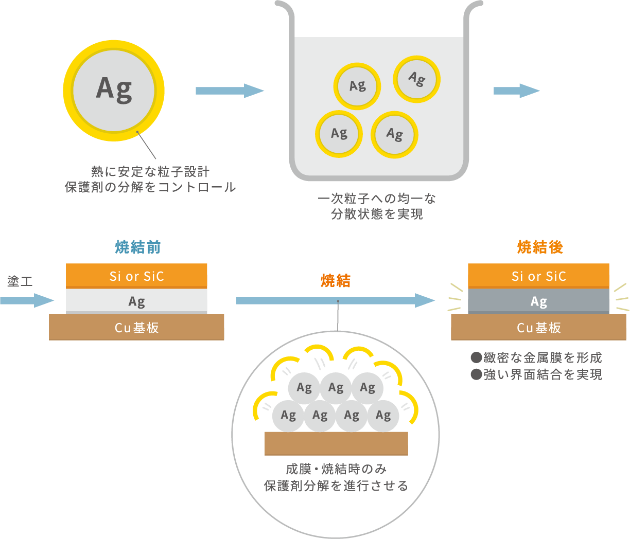
Paste design technology that achieves printability

The viscosity can be adjusted according to the printing method.
Dispense printing method
Metal mask printing example

Dispense printing example
Inquiries
artience Co., Ltd. Group R&D Division
TEL:+81-3-3272-5732
