What is plastic colorants?
plastic colorants is a general term for colorants used to knead colorants into plastics to color them (internal coloring). In addition to explaining what colorants are, their roles, functions, and types, we also explain how to manufacture masterbatches and mold plastics.
- Introduction
- Role and function of colorants
- Type of colorant
- masterbatches manufacturing process
- types of plastic
- Plastic molding method
- Features of our products
Introduction
There are various plastic products around us, such as plastic bottles, stationery, and food containers (trays). These plastic products are not originally colored. Plastic (resin) is essentially colorless (milky white). By adding colorants such as pigments, plastic products in a variety of colors are created.
There are two main ways to color plastic: external coloring and internal coloring. External coloring refers to coloring the surface of plastic, and includes printing, painting, plating, etc. On the other hand, internal coloring involves kneading coloring materials into the plastic to color it. Because the plastic and coloring material are mixed together, unlike external coloring, the interior is evenly colored. The coloring materials used for this internal coloring are collectively called "colorants."



Role and function of colorants

Coloring also has the role of "identification". To take a familiar example, the lids of hot drink bottles are uniformly orange, so you can immediately recognize that the bottle is hot. In addition, to make it easier to identify during construction or emergencies, pipes for water use are color-coded as ``blue,'' and gas pipes as ``yellow,'' according to a global standard. In addition, color is also effectively used to protect the contents, such as by painting the outside of the product black to block UV rays and prevent the contents from deteriorating.
For example, automobile bumpers and containers use carbon black as a colorant to improve weather resistance (* resistance to temperature changes and wind and rain).
Colorants can also be given "conductive" and "antistatic" functions. For example, products that incorporate precision equipment such as IC chips, such as personal computers and inspection equipment, may malfunction or malfunction even with a weak current. However, the plastic material that protects them originally has the property of being easily charged with electricity, as can be seen from the fact that it adsorbs dust when rubbed against the underlayment. In such cases, a highly conductive colorant can be kneaded into the plastic to allow electricity to escape to the outside, thereby reducing the risk of failure. In addition, there are examples of using white colorants on the backsheets of solar cells to reflect light inside and increase power generation efficiency.
Type of colorant
The main types of colorants include "masterbatches", "colored pellets and coloring compounds", "dry colors", and "paste colors and liquid masterbatches". These are mixed with natural pellets * (plastic in the form of particles before the coloring material is mixed) and molded to make plastic products.
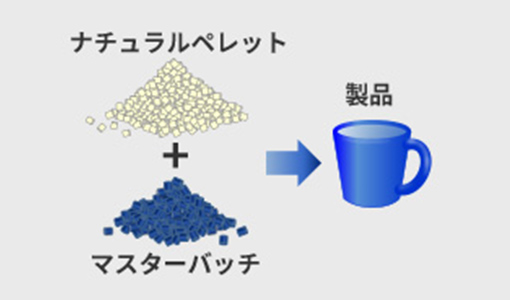
masterbatches
A coloring agent in the form of pellets (particles). Highly concentrated pigments are kneaded inside, and you can easily change the shade of the color by adjusting the amount mixed with the natural pellets. It has excellent dispersibility, allows for uniform and beautiful coloring, and is easy to handle without worrying about scattering or contaminating equipment. It also has superior cost performance compared to colored pellets.

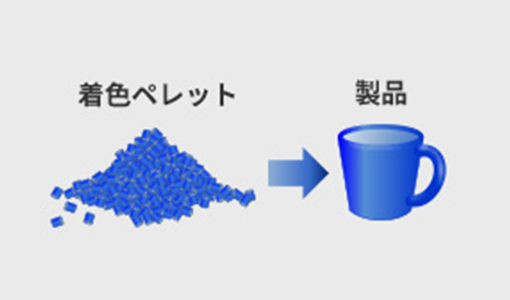
Colored pellets/colored compounds
Colorant in pellet form. Unlike masterbatches, it is already set to the same concentration (color) as the final product, so there is no need to mix it with natural pellets. It has the advantage of eliminating the hassle of compounding and making it easier to consistently produce the desired color, but it requires a large amount of inventory to make the product, making it more expensive than others.

dry color
Powdered colorant. It is made by mixing pigments and metal soap. It is the cheapest colorant because it requires little effort to manufacture, but it has some drawbacks in terms of handling, such as being easily splattered, easily staining equipment, and difficult to measure.

Paste color liquid masterbatches
It is a liquid colorant with different viscosities between paste colors and liquid masterbatches. Paste colors are mainly used when the base resin is in liquid form such as vinyl chloride, and liquid masterbatches is used overseas when you want to add a light color to the product, such as translucent.


| masterbatches | colored pellets | coloring compound | dry color | paste color liquid masterbatches |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shape | pellet | pellet | pellet | powder | liquid |
| pigments concentration | 10~70% | 5% or less | 5% or less | 30~80% | 30~60% |
| Dispersibility (coarse particles) | ◎ | ○~◎ | ○~◎ | △ | ○ |
| Dispersibility (uneven color) | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | ○ | ○ |
| High pigments concentration coloring | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | × | × |
| Spatterability | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | × | ◎ |
| contamination | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | × | × |
| Metrology | ◎ | Unnecessary | Unnecessary | △ | △ |
| Molding processability | ○ | ◎ | ◎ | △~○ | △ |
| storage stability | ◎ | ◎ | ◎ | △ | ○ |
| inventory cost | ○ | × | × | ○ | ○ |
| versatility | ○ | × | × | ○ | △~○ |
| coloring cost | ○ | × | ○ | ○ | ○ |
masterbatches manufacturing process
Currently, the main coloring agents used in Japan are masterbatches, which have excellent total balance and can be manufactured using relatively light equipment. masterbatches can be created with various colors and functions by incorporating pigments and other coloring materials and functional materials into the base pellets (resin material).
①Preparation/stirring
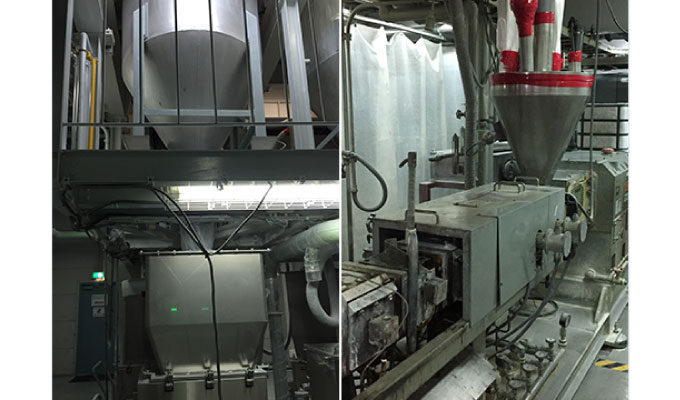

②Extrusion
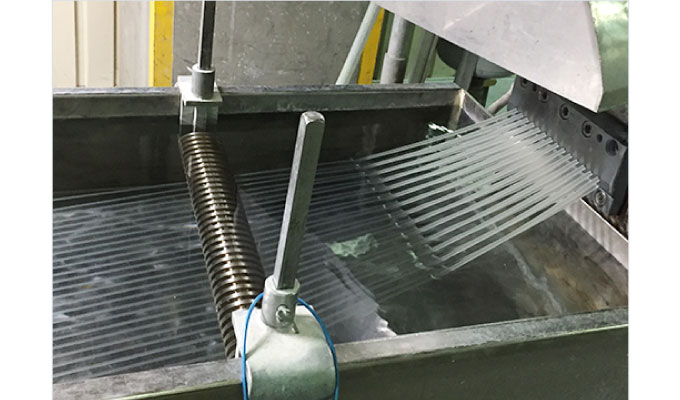

From the tip of the extruder, colored resin comes out in the form of long, thin rods like spaghetti.
③ Cooling
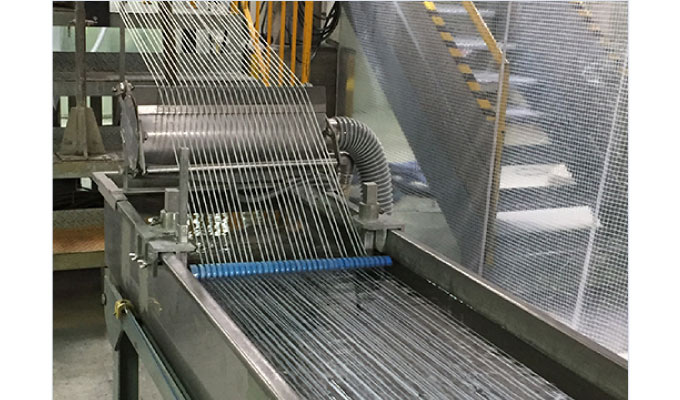

④ Cutting
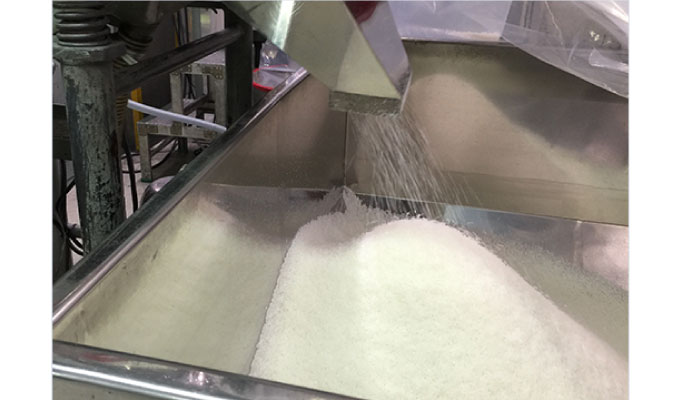

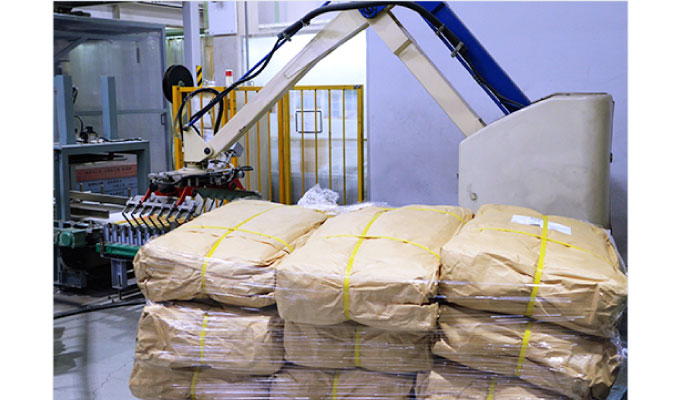
⑤Filling/packing

types of plastic
There are many different types of plastics that can be mixed with colorants. Thermoplastic plastics (molded by melting with * heat), which are often used in daily necessities, can be classified into two categories: "crystalline" and "amorphous", each with various physical properties. When designing products, the physical properties of these plastic materials must be considered.
For example, among crystalline plastics, polyethylene (PE), which is resistant to heat and chemicals, is used for films and buckets, and polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which is highly transparent and durable, is used for PET bottles and egg cartons.
| classification | Type of material | Abbreviation | Main properties | Product example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| crystalline plastic | polyethylene | PE | Resistant to heat and chemicals | film, bucket etc. |
| polyethylene terephthalate | PET | Highly transparent and durable | plastic bottles, egg cartons, etc. | |
| amorphous plastic | PVC | PVC | Flame resistant and durable | Hoses, wires, etc. |
| ABS resin | ABS | Opaque, cracking and heat resistant | furniture, computers, etc. |
Plastic molding method
There are many ways to mold plastics, including compression molding, injection molding, calendar molding, extrusion molding, blow molding, and vacuum molding.
injection molding
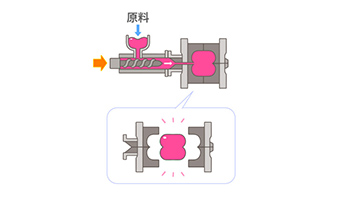
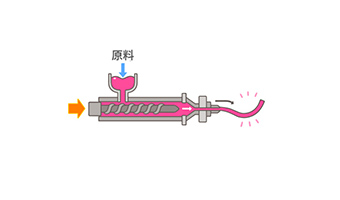
extrusion molding
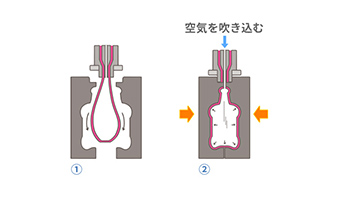
blow molding
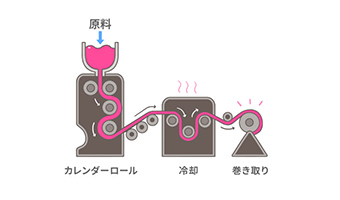
calendar molding
compression molding
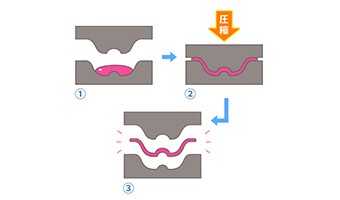
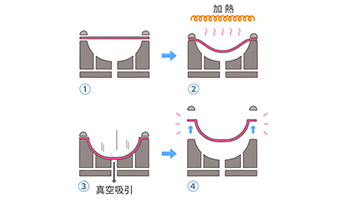
vacuum forming
Features of our products
TOYOCOLOR 's plastic colorants come in a variety of forms, including powder, paste, and pellet forms, depending on the type of plastic and molding method. We also provide solutions tailored to the type of plastic used by the customer and the shape of the colorant desired.
Furthermore, we also manufacture high-performance compounds and masterbatches that go beyond simple coloring applications and have properties such as flame retardancy, conductivity, and optical properties.
Inquiries
TOYOCOLOR CO., LTD. Coloring Sales Department
TEL:+81-3-3272-0834
